You’ll immediately notice a blown battery fuse when your vehicle won’t start, dashboard warning lights illuminate, and electrical accessories fail completely. Your headlights will dim considerably, especially at idle, while power windows and locks respond slowly or stop working entirely. The charging system warning light typically activates first, followed by the check engine light due to insufficient power supply. These symptoms often mimic complete battery failure, creating clicking sounds during attempted starts. Understanding these warning signs helps you identify the root cause before further complications arise.
Quick Tips
- Dead battery symptoms including no engine start, clicking sounds, and slow cranking indicate a blown battery fuse.
- Dimming or flickering headlights, especially at idle, signal power supply issues from a faulty battery fuse.
- Dashboard warning lights activate, starting with charging system alerts followed by check engine lights due to insufficient power.
- Electrical system malfunctions like slow power windows, locks, and labored engine cranking suggest blown fuse problems.
- Regular fuse box inspections for scorch marks, discoloration, and damaged components help identify potential fuse failures.
Dead Battery and Charging Problems
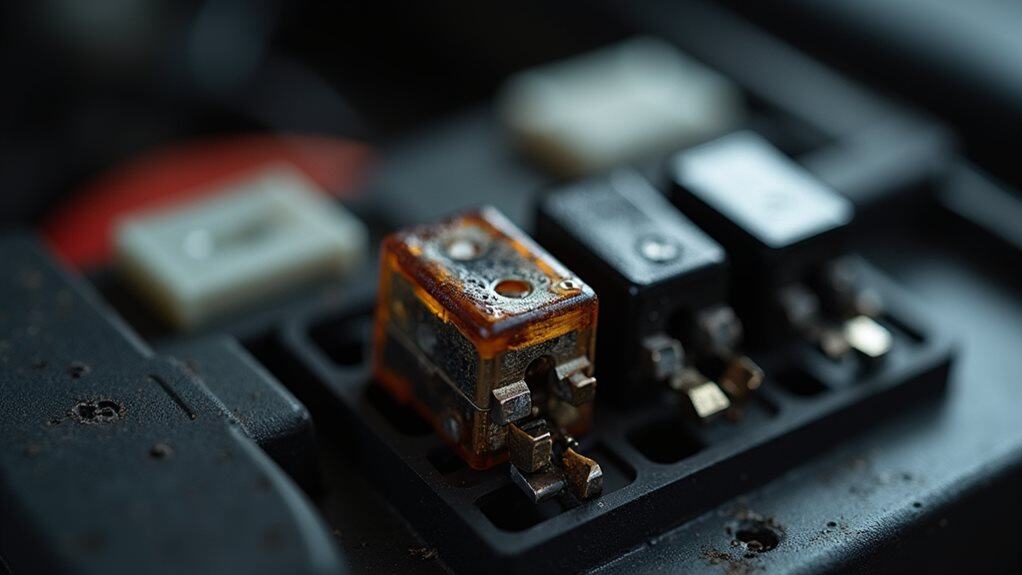
When your car’s battery fuse blows, it creates a cascade of electrical problems that can easily fool you into thinking your battery has died completely. You’ll experience identical symptoms: no engine start, clicking sounds, slow cranking, and failed electrical accessories. The blown fuse interrupts power flow throughout circuits, mimicking complete battery failure while potentially preventing proper charging system operation. A blown fuse can also prevent your battery from recharging while driving, creating a compounding problem where even a good battery gradually loses power. Regularly checking battery connections can help prevent such issues from exacerbating.
Dimming Headlights and Vehicle Lights
Beyond the obvious starting problems, a blown battery fuse creates another telltale sign that’s impossible to ignore once you’re behind the wheel.
Your headlights will dim noticeably, especially when idling at traffic lights. You’ll notice flickering or inconsistent brightness that signals interrupted power supply. This voltage fluctuation can overwhelm the bulbs and cause them to fail prematurely. Additionally, issues with the charging system can exacerbate these symptoms, as they affect the overall power delivery to the vehicle’s electrical components.
Both interior and exterior lights lose their normal intensity, indicating widespread electrical issues.
Dashboard Warning Lights Activation
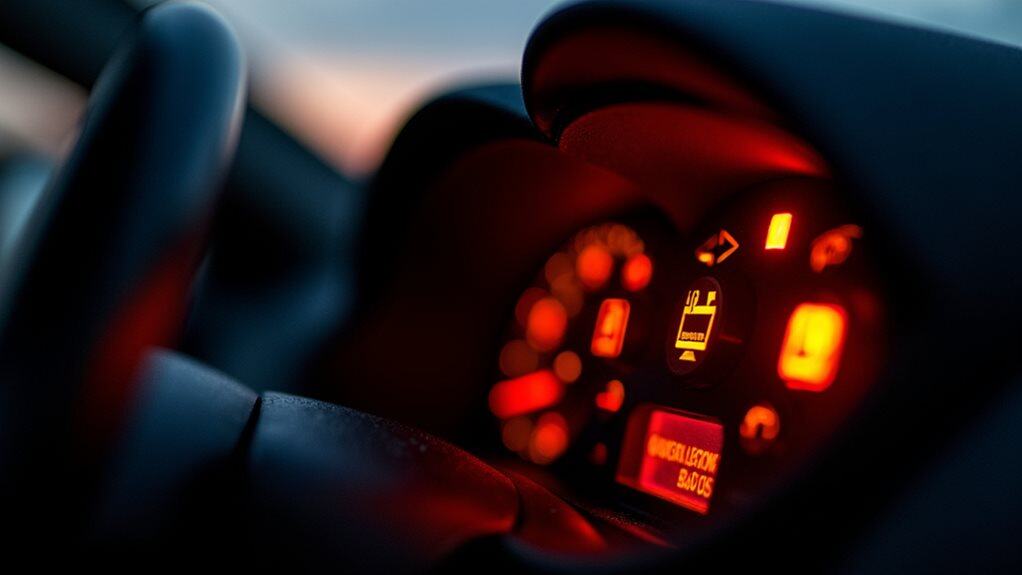

Although your vehicle’s dashboard warning lights serve as your primary communication system with the car’s electrical health, a blown battery fuse triggers a cascade of illuminated alerts that can overwhelm even experienced drivers.
You’ll notice your charging system warning light activating first, followed by potential check engine light activation as electrical systems struggle with insufficient power supply. Additionally, a malfunctioning alternator can exacerbate the issue by compromising the vehicle’s power supply.
Electrical System Malfunctions
After the initial dashboard warning lights illuminate, your vehicle’s electrical system malfunctions will become increasingly apparent through a series of progressively worsening symptoms.
You’ll notice dim or flickering headlights, indicating weakened battery voltage. Power windows and locks will respond slowly or stop functioning entirely.
Engine cranking becomes labored, and you may detect burning smells from overheated wiring. Additionally, monitoring dashboard warning lights can help identify underlying electrical issues before they escalate.
Essential Electronics Failure
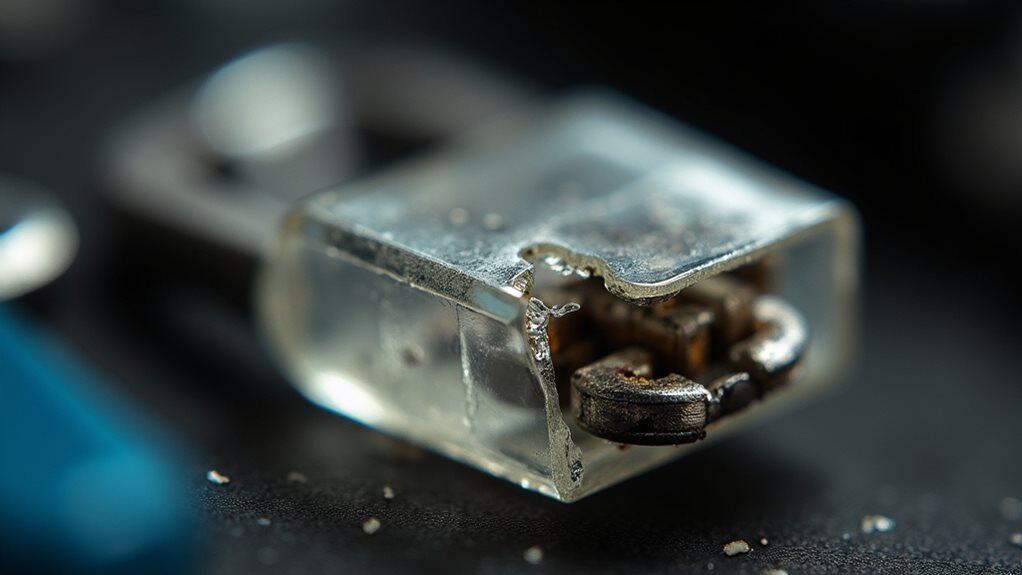

Five critical failure modes can destroy your vehicle’s essential electronics when a battery fuse blows, each creating distinct patterns of component breakdown that you’ll recognize through specific symptoms.
Excess temperature causes thermal runaway in circuits, while overvoltage creates dielectric breakdown.
Mechanical stress cracks components, defective workmanship triggers infant mortality failures, and aging accelerates material degradation throughout your electrical system.
Burning Smell Near Fuse Box
When plastic insulation materials inside your fuse box overheat and begin melting, they’ll produce a distinctive “fishy” or burning chemical smell that serves as an early warning sign of dangerous electrical problems.
This odor typically results from loose connections creating excessive heat, overloaded circuits, or degraded wiring insulation.
You should immediately contact a qualified electrician for safety evaluation.
Visual Inspection of Fuse Components
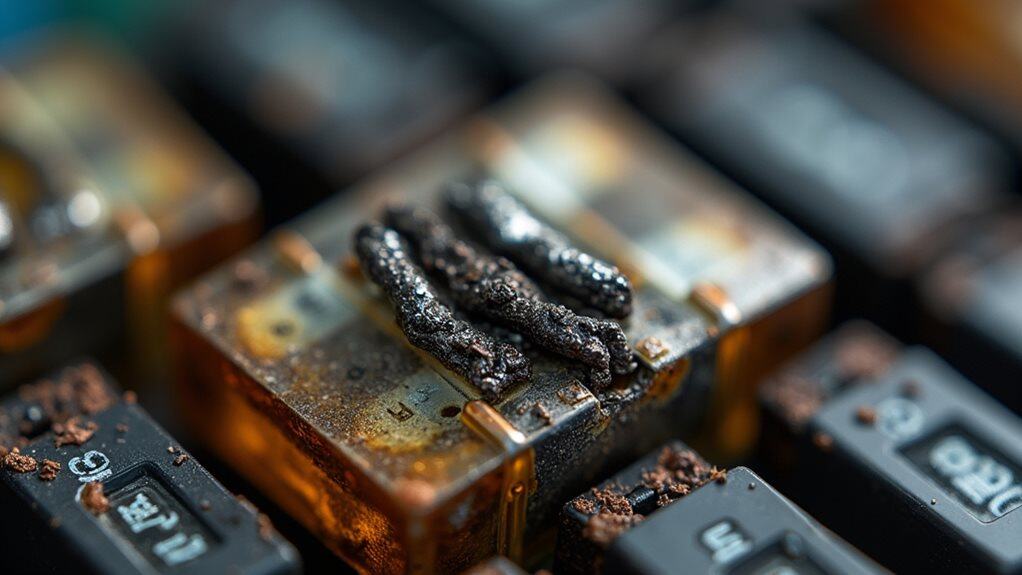

Beyond detecting warning odors, you can often identify blown fuses through careful visual examination of the components themselves.
Look for broken metal filaments inside glass tube fuses, or melted sections on blade fuse strips.
Check for black scorch marks, cloudy buildup, or discolored plastic housing.
Inspect ceramic fuses for cracks, chips, or dark burn marks indicating failure.
Multimeter Testing for Continuity
Although visual inspection can reveal obvious signs of fuse failure, electrical testing with a multimeter provides definitive confirmation of a blown fuse through continuity measurement.
First, select continuity mode on your multimeter, then place probes on fuse terminals. A beep indicates good continuity, while silence or “OL” reading confirms the fuse is blown.
Short Circuits and Overloading Issues
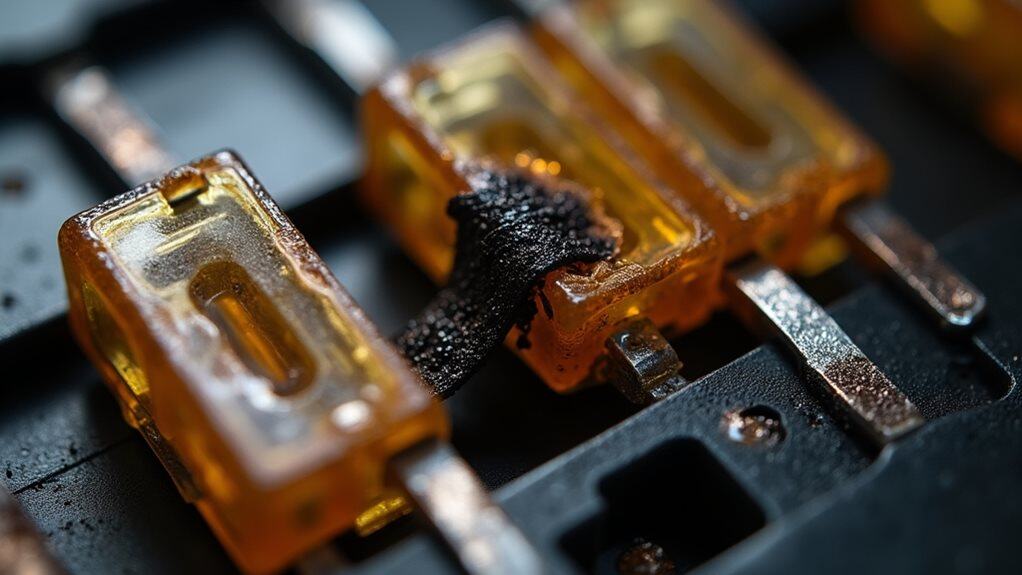

Understanding the electrical conditions that cause fuse failures requires examining the two primary culprits: short circuits and system overloading.
Short circuits create low-resistance paths that trigger sudden current surges, causing fuses to blow instantly.
System overloading occurs when electrical demands exceed circuit design limits, generating excessive heat that melts fuse elements and protects your electrical system from damage.
Improper Jump-Starting Damage
When you attempt to jump-start your vehicle incorrectly, you’re fundamentally introducing uncontrolled electrical energy into a system designed for precise voltage and current flow.
Reversing cable polarity sends damaging current through sensitive circuits, while voltage spikes can destroy your Engine Control Unit, safety systems, and fuel delivery components, creating expensive repair bills.
Preventive Maintenance and Safety Measures
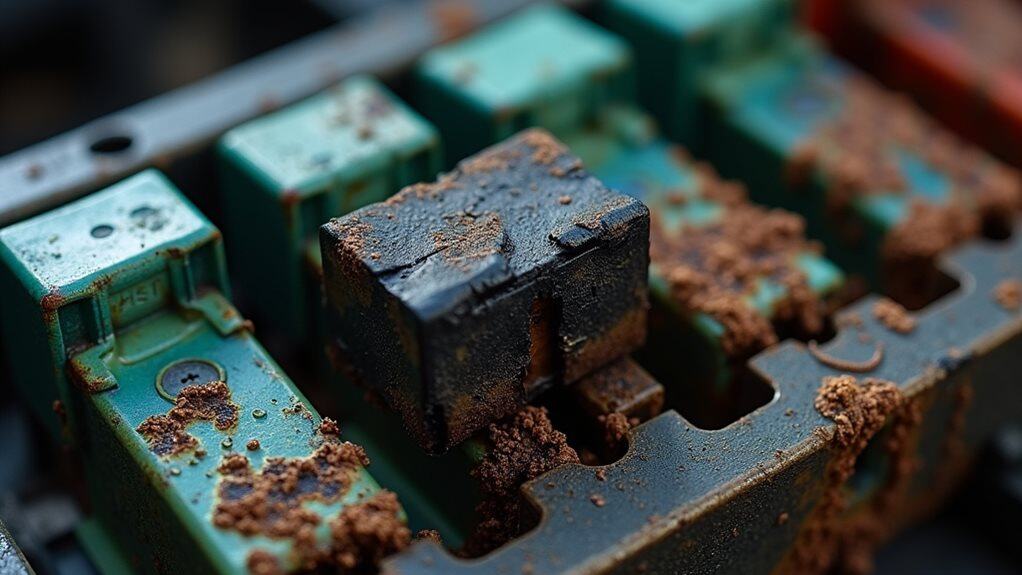

You can greatly reduce the risk of blown battery fuses by implementing consistent preventive maintenance practices that focus on three critical areas of your vehicle’s electrical system.
Regular fuse box inspection involves checking for corrosion, moisture buildup, and damaged components that could lead to electrical failures, while proper battery charging practices guarantee your charging system operates within safe parameters to prevent voltage spikes that damage fuses.
Electrical system safety protocols encompass thorough maintenance procedures, including terminal cleaning, secure connections, and load management techniques that protect your vehicle’s circuits from overloads and premature component failure.
Regular Fuse Box Inspection
Since electrical systems operate continuously in your home, regular fuse box inspections serve as your first line of defense against potential failures, fires, and costly repairs.
You should check monthly for scorch marks, discoloration, or charring that indicates overheating. Look for damaged fuse holders, loose connections, and corrosion around terminals while ensuring covers remain secure.
Proper Battery Charging Practices
Beyond identifying problems through regular inspections, implementing proper battery charging practices will help prevent blown fuses and extend your battery’s operational life.
Always turn off your vehicle’s ignition before connecting charger clamps, attaching positive first, then negative. Monitor charging time carefully to avoid overcharging, which can damage electrical components and blow protective fuses throughout your vehicle’s system.
Electrical System Safety Protocols
When working with automotive electrical systems, proper safety protocols serve as your primary defense against electrical hazards and system damage.
Always disconnect the battery before starting electrical work, and implement lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental power-up.
Wear insulated gloves rated for voltage, safety glasses, and flame-resistant clothing.
Maintain clean, dry work environments to reduce shock risks.
Wrapping Up
You’ll prevent costly repairs and dangerous situations by recognizing blown battery fuse symptoms early. Watch for dead batteries, dimming lights, dashboard warnings, and electrical malfunctions. Don’t ignore these signs—they indicate serious problems that can strand you or damage your vehicle’s systems. Test fuses with a multimeter when you suspect issues, and always follow proper jump-starting procedures. Regular inspection of your electrical system protects both your safety and your wallet from unexpected breakdowns.

