There are various imbalances to correct when an engine runs. These are the primary balance, and the engine’s firing order and combustion intensity determine the secondary balance. A harmonic balancer is a particular kind of small flywheel, ring, or pulley mounted on rubber that is attached to the crankshaft on the accessory end of an engine.
These are frequently found in engines with lengthy crankshafts or more cylinders than four. Vibration and torque will move along the crankshaft length following the firing impulses and their order.
The flywheel at the crankshaft’s output side helps reduce vibration. The harmonic balancer’s function is moderate vibrations at the opposite end of the crankshaft. A spinning weight at each end of the crankshaft helps prevent uneven crankshaft twist and wear when the engine is moving quickly or at high speeds.
It can even prevent bad harmonic balancer symptoms such as your crankshaft fracturing. In our guide, you can learn more about misfires and if the clicking noise you get from your harmonic balancer can cause one. By the end, you’ll know more about one of the most overlooked areas of cars that cause issues and a possible misfire code. (Read Car Makes Whining Noise When Starting Cold)

Signs of a Bad Harmonic Balancer
You may ask, what happens when harmonic balancer fails? A failure can cause a range of issues. So, here, you can find the common symptoms of a bad harmonic balancer:
Engine Vibration
The harmonic balancer’s role is to reduce crankshaft vibrations. As a result, if the balancer malfunctions, you might notice a noticeable vibration coming from the engine compartment as you speed up, ideal, or hit the brakes.
Harmonic Balancer Wobble
The balancer typically starts to separate as soon as the rubber isolator fails, resulting in a visible wobble when the engine is running.
Extraordinary Noises
A bad balancer might result in a sound that changes with engine speed, such as banging, rattling, or squeaking. Sometimes the noise is so loud that it can be misconstrued as an internal engine issue. Additionally, a balancer failing can lead to strange drive belt or automatic drive belt tensioner movement, which can produce clicking or screaming sounds when the engine is running.
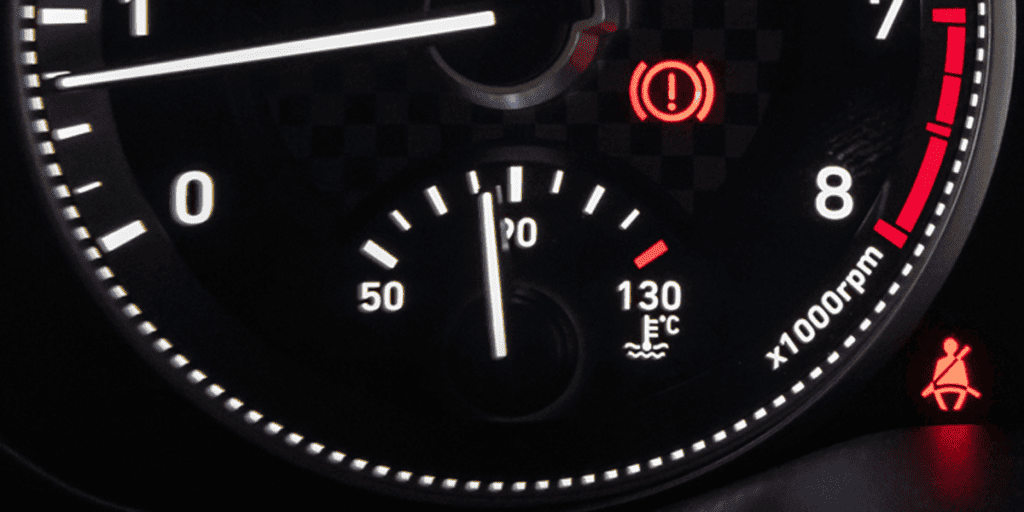
Check Engine Light is Illuminated
Crankshaft position and speed are determined by a crankshaft position (CKP) sensor signal, which is sent to your car’s primary computer, also known as the powertrain control module (PCM). A toothed or notched wheel often found on the crankshaft or harmonic balancer is read by the CKP sensor.
The sensor may provide an abnormal signal if the harmonic balancer malfunctions, which will cause the PCM to illuminate the check engine light.
Wear or Damage
You might be able to observe noticeable wear or damage if you look at the harmonic balancer. A separation between the hub and outer part of the balancer might have occurred, for instance, due to the rubber insulator.

What is a Harmonic Balancer?
Why use a harmonic balancer? Balancers absorb crankshaft vibrations. Each piston completes intake, compression, power, and exhaust in a four-stroke engine while turning the crankshaft.
The harmonic balancer moderates crankshaft high-frequency vibrations. A central hub, an inertia ring, and a rubber insulator are components of a typical balancer. A crankshaft’s central hub is bolted on. As the crankshaft turns, the inertia ring and rubber ring dampen vibrations.
Additionally, the harmonic balancer has a pulley that connects to the drive belt of the engine. The pulley turns the belt when the engine operates, which rotates engine-driven accessories (alternator, A/C compressor, etc.).
What Happens When a Harmonic Balancer Fails
Although the harmonic balancer looks straightforward, a malfunction might have severe consequences for your car. Most harmonic balancers fail as rubber loses adhesion to metal parts. Such occurrence makes car timing engine ignition challenges. The outer ring can work off the inner hub and cause belt misalignment. (Read Wire From Battery To Starter Motor)
Engine issues such as worn rod bearings and a broken crankshaft may result in the balancer damping undesired crankshaft vibrations. The belt and engine-driven accessories might both be harmed by a faulty balancer. The balancer could also fly apart, destroying various engine components.
It would help if you always got a mechanic to give you a replacement harmonic balancer as soon as you know you have a faulty one.
When a cylinder fires, the crankshaft speeds up for a short period and slows as the next cylinder in the firing order fires as it igniting the fuel. A crankshaft’s speeding up and slowing generates torsional vibration or twisting, which stresses the crankshaft and connected components.
If the stress is sufficient, the crankshaft can fail.
The crankshaft assembly’s mass can be increased as a way to reduce vibrations in some engines. Still, this approach increases the crank’s rotating mass and the vehicle’s overall weight. A crankshaft pulley with a harmonic dampener/balancer is the alternative treatment.
A harmonic balancer acts like a punching bag for your crankshaft. A harmonic balancer has two primary components: inertial mass and an energy-dissipating element. The inertial mass consists of an outer ring that could have the grooves for the belts and an inner hub that connects to the crankshaft. The outer ring contains the mass to cancel out the vibrational forces.
Between the two metal components is the energy-dissipating element, which is a rubber or elastomeric compound. As it absorbs crankshaft vibrations, this rubber ring can push the two metal components out of phase by up to 20°.
Flexing causes the energy-dissipating element to generate heat. A harmonic dampener may appear straightforward at first glance, but engineering is involved in tailoring the device to an engine over a certain RPM range.
One way to reduce vibrations in some car engines is by adding mass to the crankshaft assembly at the cost of increasing the vehicle’s weight. A crankshaft pulley using a harmonic dampener is an alternative fix.
A harmonic dampener may appear straightforward at first glance. Still, engineering is involved in tailoring the device to an engine over a specific range of RPMs where inner components such as a fluid, spring, or clutch come into operation. (Read Too Much Heet In Gas Tank)
Signs Your Harmonic Dampener Has Failed or Failing
Timing Marks Out of Line
The timing marks will move if the outer ring has detached from the inner ring. Comparing the timing marks on the valvetrain timing belt will show this as the crank position sensor will relay the incorrect information to the car ECM.
Worn Belt Edges
The grooves on the outer ring may shift so far that they are out of alignment with the pulleys on the other accessories, such as your water pump. There could be uneven polishing or wear in the pulley grooves, which need to be replaced.
Engine Vibration
Test the dampener for damage if you have an odd engine vibration but no misfire code. It may take a mechanic to diagnose. You may hear sounds on your Ford, like a screw bouncing around.
Transmission damage
The transmission faces destructive forces if a dampener can’t dampen crankshaft vibration. Vibrations can damage the input shaft, bearings, planetary gears, and more. Even your differential’s gears can end up damaged on cars with large displacement engines and manual transmission.
Alternator or Power Steering Pump Failure
There are limits on the amount of vibration a belt tensioner or pulley can withstand before bearings are damaged. Even though the dampener may only flex 1 or 2 degrees, the strain on the associated power steering components or the vehicle alternator is reduced.
Rough Idle
A dampener is made to function at given engine speeds or certain RPMs. Some dampeners are more active when the engine is idle, and plugs can’t ignite the fuel as they should. The idle may change if a dampener fails because the dampening mass moves as you step on the gas when pulling out of a parking spot onto the road.

Belt Slap Or Belt Tensioner Movement
If the dampener doesn’t work, the power pulses, and the vibration is transferred to the tensioner. You can see this as a flutter in the vehicle tensioner arm.
Why A Harmonic Dampener Fails
Heat
The elastomeric components in a dampener turn vibrations into heat. Rubber fails if the heat isn’t dispersed through the vents in the wheel well liner.
Cracking
Outer or inner inertia mass bearing ring cracks where the ring separates from the dampener assembly. It is rare but possible, and when it happens, surrounding components can be damaged, like the radiator.
Rubber Deterioration
Dampener materials can degrade because of ozone, heat, and flexing. On most Ford vehicles, the dampener lasts the life of the vehicle and does not need to be replaced. Also, you shouldn’t see the rubber crack or bulge.
Oil Leaks
A leaking crankshaft seal can soak the rubber in oil, which will cause it to deteriorate. Also, leaking valve covers, power steering pumps, and other oil cause rubber to fail. Such fluids also cause the bond between metal and rubber to weaken.
Installation Error
You should never strike a dampener with a hammer, as it can damage internal components. Common installation errors are using the center bolt to push the dampener onto the crank nose. Do this, and you can strip the threads because of the force required.
Removal Error
Use the right process and tools to pull the dampener off the vehicle. The dampener must be removed in most cars to replace the timing belt. Never force or hammer the outer ring, or put it under extreme pressure. (Learn How To Use Engine Hoist)
Transmission Issues
The rear main bearing is opposite the flywheel, flex plate, and torque converter. Out-of-spec parts can generate a crankshaft imbalance that the dampener can’t correct. If the owner recently had transmission maintenance done, it’s likely the wrong parts were used or installed incorrectly.
Belt Tension
An overly tight belt can stress the harmonic dampener and the accessory belt drive components because of the added tension on the crank.