When your car leaks gas only while running, you’re experiencing a pressure-related fuel system failure where the fuel pump creates higher pressure during operation, causing compromised seals, cracked fuel lines, or loose connections to leak under stress. Look for the distinctive sweet gasoline odor, wet spots around fuel lines, and visible wetness near injectors while the engine runs. This dangerous situation requires immediate attention since gasoline vapors create fire and explosion risks, plus environmental contamination concerns that demand prompt professional diagnosis and repair.
Quick Tips
- Check fuel lines and connections for cracks or loose clamps that fail under operating pressure.
- Inspect fuel injectors for wetness or compromised seals that leak during fuel pulse cycles.
- Look for distinctive gasoline odor and wet spots around fuel tank and lines while engine runs.
- Use pressure testing equipment to measure fuel system integrity and identify leak locations accurately.
- Seek professional help immediately if fuel puddles appear or persistent odors indicate safety risks.
Understanding Why Gas Leaks Occur Only During Engine Operation

When your car only leaks gas during engine operation, the root cause typically stems from the dramatic changes in pressure, temperature, and mechanical stress that occur when the engine runs.
Your fuel system operates under considerably higher pressure while running, forcing fuel through compromised seals, cracked lines, or loose connections that remain sealed when parked. These fuel line deteriorations often develop gradually through normal wear and require regular inspection to identify before they become problematic leaks. Additionally, a faulty ignition switch can exacerbate fuel system issues, leading to further complications while driving.
Common Components That Cause Running-Only Fuel Leaks
Since your car’s fuel system operates under considerably higher pressure during engine operation, several specific components become prime suspects for running-only leaks.
Deteriorated rubber fuel lines, loose clamps, and corroded metal lines commonly fail under pressure. Additionally, brake fluid leaks can indicate a serious issue in other vehicle systems, emphasizing the importance of regular inspections. Faulty fuel injectors with compromised seals leak during fuel pulses, while fuel pump assemblies with missing clips cause significant running-only leaks. These leaks create fire hazards that require immediate attention from vehicle owners.
How to Identify Gas Leak Locations and Warning Signs
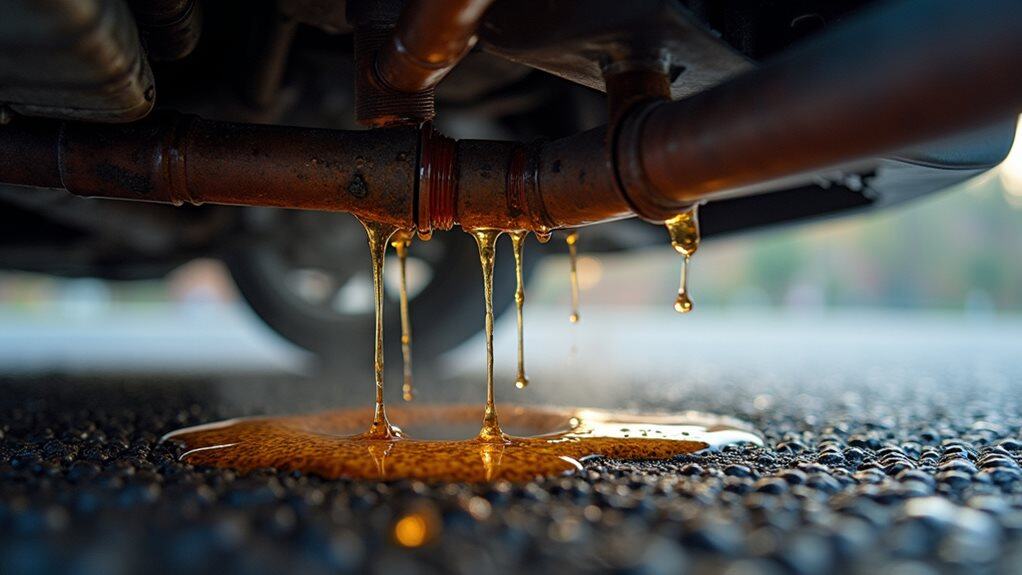

Understanding which components fail under pressure helps you locate the source of your fuel leak, but you’ll need to recognize the warning signs and know where to look.
Start by smelling for gasoline’s distinctive sweet odor, which often appears before visible signs.
Check for wet spots, stains, or discoloration around the fuel tank, lines, and injectors while the engine runs. Additionally, be aware that mixing antifreeze types can lead to severe issues in your vehicle’s performance, highlighting the importance of maintaining proper fluid levels and types.
Pressure-Related Factors That Trigger Leaks While Running
Although fuel systems maintain relatively stable pressure when your car sits idle, the fluctuating conditions created by a running engine introduce multiple pressure-related factors that can trigger leaks.
Operating engines generate heat expansion, causing pressure spikes that exploit weak seals. Additionally, malfunctioning fuel pressure regulators, faulty check valves, and clogged filters create excessive pressure, forcing fuel past deteriorated components. Regularly monitoring refrigerant levels is essential to prevent system strain that can lead to leaks.
Safety Hazards and Environmental Risks of Fuel Leaks

When you find your car leaking gas, you’re facing serious safety hazards that demand immediate attention, including fire and explosion risks from gasoline’s highly flammable nature.
Beyond the immediate danger to you and others, fuel leaks create environmental contamination that can pollute soil and groundwater systems for years.
You’ll also encounter significant health and safety concerns from inhaling toxic fuel vapors, which can cause headaches, dizziness, and respiratory problems.
Fire and Explosion Risks
Because gasoline is highly flammable and ignites easily from heat or electrical sparks, fuel leaks create serious fire and explosion hazards that can turn a minor mechanical problem into a life-threatening emergency.
Your engine’s heat, exhaust components, and electrical systems provide multiple ignition sources.
Even small leaks release vapors that accumulate quickly, creating immediate explosion risks.
Environmental Contamination Effects
While fire and explosion risks pose immediate threats, fuel leaks create equally serious long-term environmental damage that extends far beyond your vehicle’s location.
Just one quart of gasoline can contaminate up to a million gallons of water, introducing toxic hydrocarbons into soil and groundwater.
These pollutants persist for years, disrupting ecosystems and requiring expensive remediation efforts.
Health and Safety Concerns
Beyond the environmental damage that fuel leaks inflict on surrounding ecosystems, these hazardous situations create immediate dangers that threaten your personal safety and the well-being of everyone around your vehicle.
You’re exposed to toxic vapors causing headaches, nausea, and respiratory irritation.
Fire and explosion risks increase dramatically when gasoline contacts hot engine components or electrical systems nearby.
Essential Diagnostic Tools for Detecting Gas Leaks
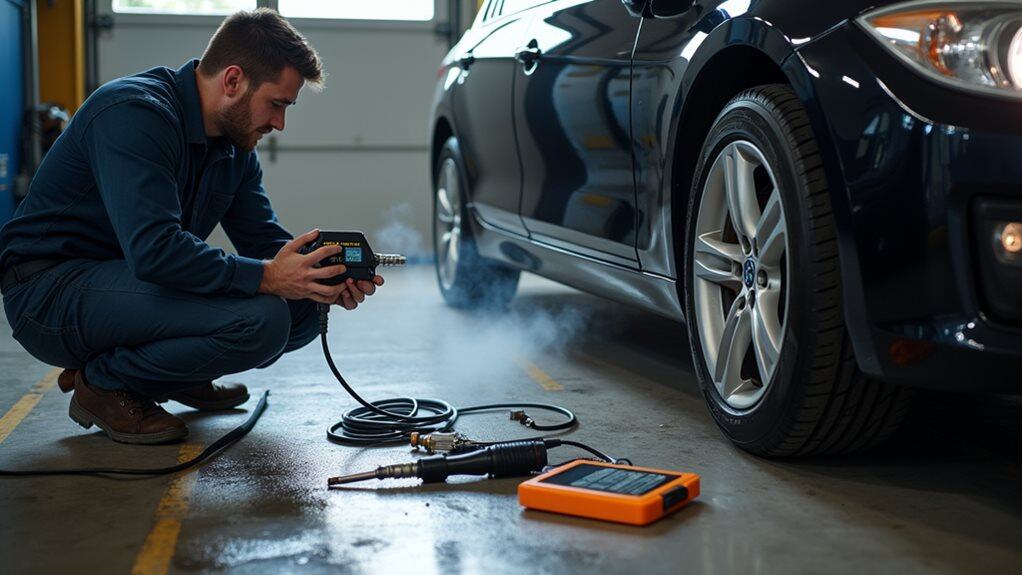

When diagnosing fuel leaks in your vehicle, you’ll need specialized tools that can accurately pinpoint the source and extent of the problem.
Pressure testing equipment allows you to systematically check your fuel system’s integrity by measuring whether lines, connections, and components maintain proper pressure without dropping due to leaks.
Visual detection methods complement pressure testing by helping you identify physical signs of fuel escape, such as wet spots, stains, or vapor clouds that indicate where your fuel system has been compromised.
Pressure Testing Equipment
Professional automotive diagnostics require specialized pressure testing equipment to accurately detect and locate gas leaks in vehicle fuel systems.
You’ll find pressure change measurement systems that monitor pressure drop rates after pressurizing components.
Helium tracer gas detectors offer ultra-sensitive leak detection, while portable sniffers pinpoint exact leak locations.
Flow analyzers monitor airflow variations to identify system breaches effectively.
Visual Detection Methods
Visual detection methods serve as your first line of defense in identifying gas leaks, offering immediate and cost-effective diagnostic capabilities that don’t require expensive equipment.
You’ll inspect for wet spots, stains, and puddles beneath your vehicle, particularly under the fuel tank and along fuel lines.
Look for cracks, wear, discoloration, or rust on hoses and connections.
Step-by-Step Visual Inspection Techniques
A systematic approach to detecting fuel leaks requires careful examination of multiple vehicle components, since gas leaks often occur only when the engine’s running and fuel system pressure increases.
Start by inspecting fuel lines for cracks, wear, or discoloration around joints.
Check the fuel tank for damage, examine injectors for wetness, and use cardboard underneath to capture drips.
Using Fuel Pressure Testing to Locate Leaks
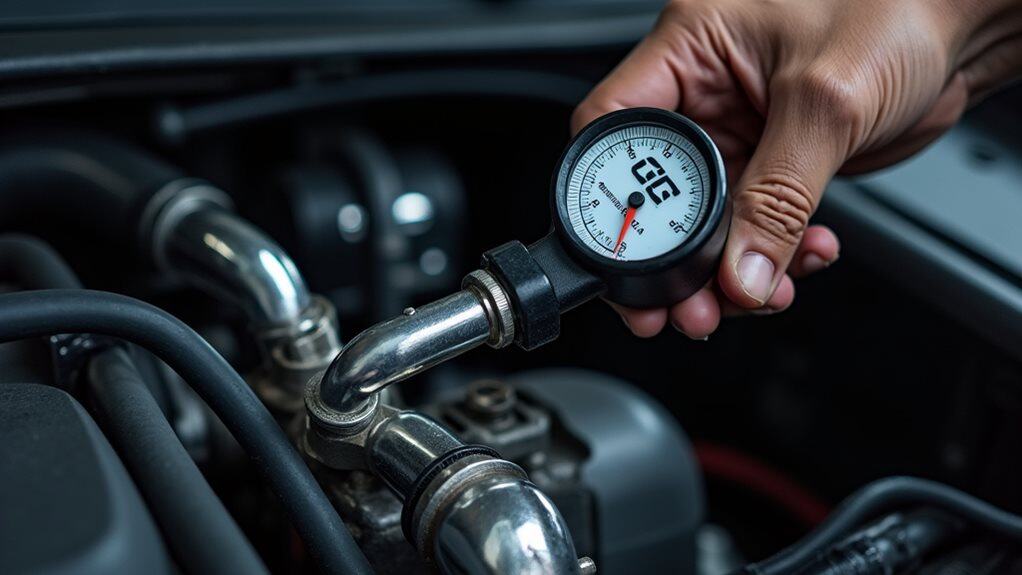

When visual inspections don’t reveal the source of your gas leak, fuel pressure testing offers a systematic approach to pinpoint hidden problems within your vehicle’s fuel system.
You’ll need to properly set up a pressure gauge at the fuel rail’s test port, then monitor how the system maintains pressure during different operating conditions.
The test results you gather will tell you whether leaking injectors, a failing fuel pump, or damaged fuel lines are causing your gas leak problem.
Pressure Gauge Setup Process
Before you can effectively diagnose fuel leaks using pressure testing, you’ll need to properly set up your fuel pressure gauge system.
Start by gathering a fuel pressure test kit with compatible adapters and a Schrader valve removal tool.
Depressurize the fuel system first by removing the fuel pump fuse and running the engine until it stalls.
Interpreting Test Results
Once you’ve completed the pressure gauge setup and collected your test readings, proper interpretation of these results becomes essential for identifying fuel leaks and their locations.
Rapid pressure loss after engine shutdown typically signals a leak somewhere in your fuel system.
Watch for fuel puddles under your vehicle during testing, which confirms external leaks requiring immediate attention.
Repair Solutions for Different Types of Fuel Leaks
Although fuel leaks can occur in various components of your vehicle’s fuel system, each type requires a specific repair approach based on the location and severity of the damage.
Tank leaks need specialized metal repair kits with resin and fiberglass cloth.
Fuel line issues require fuel-resistant sealants and tapes, while injector problems demand seal replacements or professional diagnostics.
Prevention Strategies to Avoid Future Gas Leaks

While fuel leaks can create serious safety hazards and expensive repairs, you can greatly reduce their likelihood through consistent preventive maintenance and proper handling practices.
Regularly inspect fuel lines, clamps, and injectors for wear or damage. Always secure your gas cap tightly after refueling, and avoid overfilling your tank to prevent vapor overflow.
When to Seek Professional Help for Fuel System Repairs
Even with the best prevention strategies in place, some fuel system problems will require professional skills to resolve safely and effectively.
You’ll need expert help when persistent fuel odors continue despite your DIY attempts, visible puddles appear under your vehicle, or dashboard warning lights illuminate.
Complex electrical components and safety risks demand certified technicians.
Wrapping Up
You’ve learned that gas leaks occurring only while running typically result from fuel system pressure issues. When you identify these leaks early, you’ll prevent dangerous situations and costly repairs. Remember, you shouldn’t attempt complex fuel system repairs without proper tools and experience. If you’re unsure about any diagnostic steps or notice strong fuel odors, contact a qualified mechanic immediately. Regular maintenance and pressure testing will help you catch problems before they become serious safety hazards.