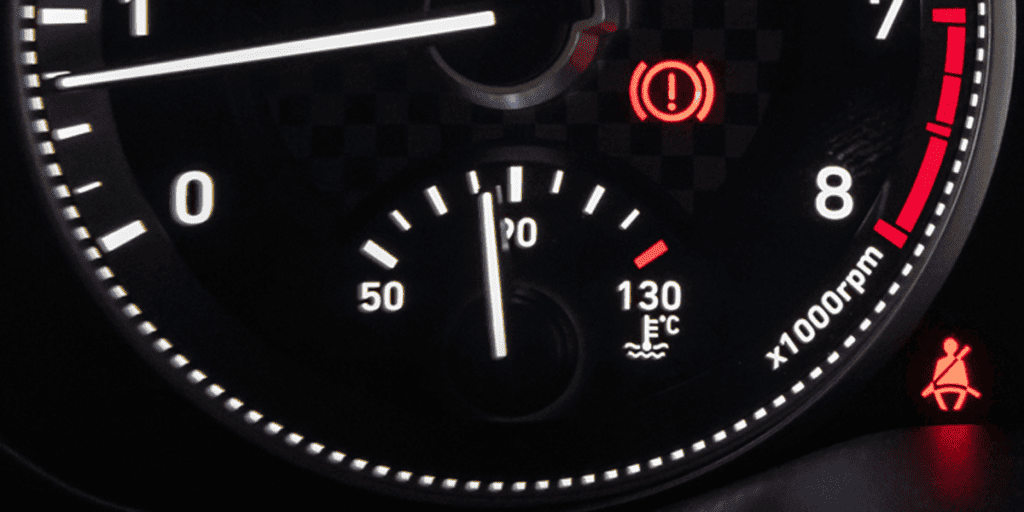
When your Toyota Avalon’s VSC light turns on, it’s flagging traction‑control, ABS, engine or emissions faults—common causes include wheel slip, loose gas cap or evap leaks, oxygen or other sensor failures, and module communication errors; you should scan the OBD‑II port for P‑codes (like evap P0456 or sensor codes), check tire pressure and obvious wiring or brakes, fix the specific DTC, then clear codes with a scanner or professional tool, and if it stays on get expert diagnostics to learn more.
Quick Tips
- VSC lights indicate traction/stability issues, often triggered when the system detects wheel slip or sensor faults.
- Common causes include wheel speed sensor failures, ABS/traction control module errors, or wiring/connectors.
- Evap leaks (loose gas cap or P0456) or oxygen‑sensor faults can illuminate VSC along with Check Engine Light.
- Simple fixes: check tire pressure, tighten gas cap, inspect obvious wiring/brakes, then read and clear codes with an OBD‑II scanner.
- If lights persist or multiple warnings appear, get professional diagnostics to retrieve DTCs and repair control‑module or brake system faults.
What Triggers the VSC Light on a Toyota Avalon

Start by recognizing that the VSC (Vehicle Stability Control) light on your Toyota Avalon comes on whenever the stability system or its related systems detect a condition that could compromise vehicle control.
It illuminates for wheel slip, loose gas cap–linked evap faults, engine or sensor malfunctions, or module communication failures.
The system adjusts throttle and brakes, and resets only after fixes or battery/scan-tool reset.
A first diagnostic step is to have the OBD system scanned to read any Pxxxx trouble codes, which will guide repairs and prevent unnecessary part replacement OBD trouble codes.
A faulty VSV can also trigger related warnings by allowing fuel vapor leaks that affect evap system operation.
How to Read Related Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
When the VSC light comes on, you’ll want to pull codes from the Avalon’s computer so you can pinpoint the problem; an OBD‑II scanner lets you read stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the engine control module (ECM) and sometimes other control units, providing specific fault identifiers like P0456 for an evap leak or oxygen‑sensor codes such as P1135/P1155 that affect engine behavior.
Use the OBD‑II port, read codes with ignition ON, document them, cross‑reference Toyota resources, and repeat after repairs; some stores scan free and advanced tools can clear lights once fixes are verified. A scan tool can also indicate whether the issue is causing drivability problems or a simple emissions-related fault. Regular HVAC checks—like replacing a clogged cabin air filter to maintain proper airflow—help prevent unrelated symptoms that can sometimes complicate diagnostics cabin air filter.
Common Symptoms to Watch For

After you’ve pulled the vehicle’s diagnostic trouble codes and documented them, watch for specific symptoms that point toward the underlying problem rather than relying on the VSC light alone.
Note dashboard combinations—VSC, Check Engine, VSC OFF—and whether lights flash or stay steady.
Observe shaking, rough idle, traction loss, altered braking, erratic acceleration, or sudden traction control activation; these narrow probable sensor or engine faults.
Also check the charging system voltage to rule out alternator issues that can mimic VSC-related faults, since a failing alternator can cause dashboard warnings and erratic electrical behavior (alternator voltage).
Simple Fixes and How to Reset the VSC Light
You can often clear a VSC (Vehicle Stability Control) warning yourself once you’ve fixed the underlying issue, but you should follow the right steps so the light doesn’t just come back.
Check tire pressure, gas cap, sensors, and brakes first.
Use an OBD2 scanner at the port under the dash to read/clear codes, or try the odometer reset, battery disconnect, or brake-pedal diagnostic sequence.
Also inspect suspension components and use a diagnostic scanner to identify any control module faults before clearing the codes.
When to Seek Professional Repair

Although some VSC warnings clear after simple checks, you should bring your Avalon to a professional if the light stays on or other indicators appear, because trained technicians use professional-grade scan tools to pull precise diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the vehicle’s computer and pinpoint the true fault.
Seek service when multiple lights, persistent illumination, erratic ABS/traction behavior, or visible wiring/brake issues occur.
Wrapping Up
You can often diagnose VSC illumination by reading the ABS/VSC codes with an OBD-II or scan tool, then inspecting wheel sensors, brake components, and steering/traction systems for faults. Try simple fixes first: tighten connectors, clean sensor rings, or replace a faulty wheel-speed sensor, then clear codes to see if the light stays off. If codes persist, or steering and braking feel compromised, get professional diagnostics and repair to guarantee safety and proper vehicle control.